7.8 KiB
External Service Contract: How to set and execute
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Step 1: Create the contract and get its unique ID
- Step 2: Fill contract
- Step 3: Both parties approve contract
- Step 4: Bill for the service
- Step 5: Cancel the contract
Introduction
It is now possible to create a generic contract between two TFChain users (without restriction of account type) for some external service and bill for it.
The initial scenario is when two parties, a service provider and a consumer of the service, want to use TFChain to automatically handle the billing/payment process for an agreement (in TFT) they want to make for a service which is external from the grid. This is actually a more direct and generic feature if we compare to the initial rewarding model where a service provider (or solution provider) is receiving TFT from a rewards distribution process, linked to a node contract and based on a cloud capacity consumption, which follows specific billing rules.
The initial requirements are:
- Both service and consumer need to have their respective twin created on TFChain (if not, see here how to do it)
- Consumer account needs to be funded (lack of funds will simply result in the contract cancelation while billed)
In the following steps we detail the sequence of extrinsics that need to be called in TFChain Polkadot portal for setting up and executing such contract.
Make sure to use right links depending on the targeted network.
Step 1: Create contract / Get unique ID
Create service contract
The contract creation can be initiated by both service or consumer.
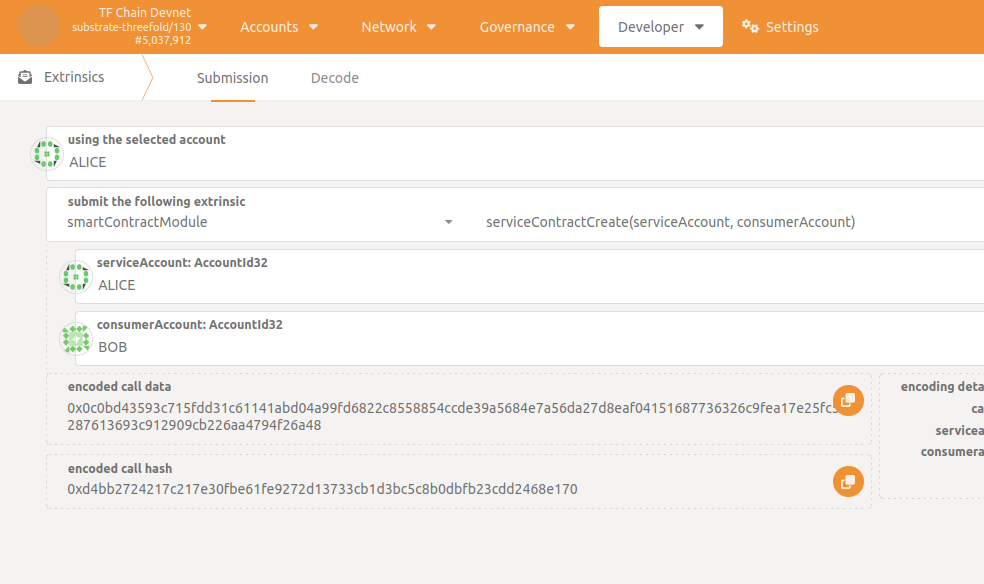
In TFChain Polkadot portal, the one who iniciates the contract should go to Developer -> Extrinsics -> smartContractModule -> serviceContractCreate(), using the account he pretends to use in the contract, and select the corresponding service and consumer accounts before submiting the transaction.
Once executed the service contract is Created between the two parties and a unique ID is generated.
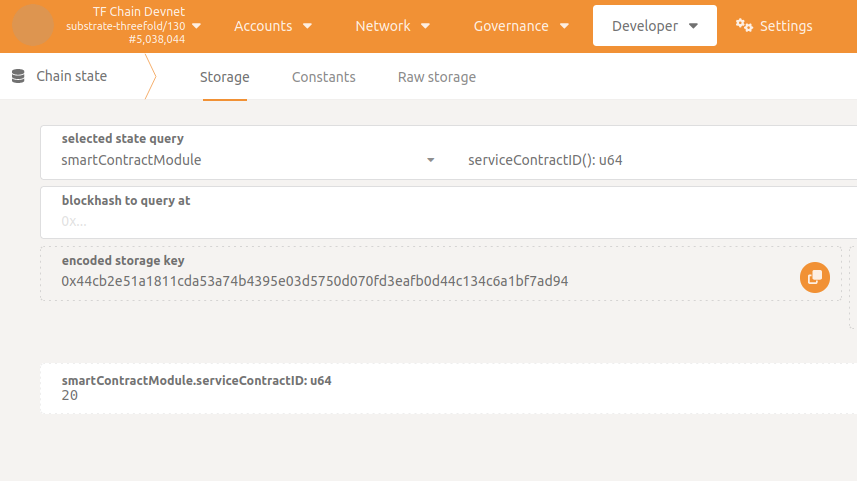
Last service contract ID
To get the last generated service contract ID go to Developer -> Chain state -> smartContractModule -> serviceContractID().
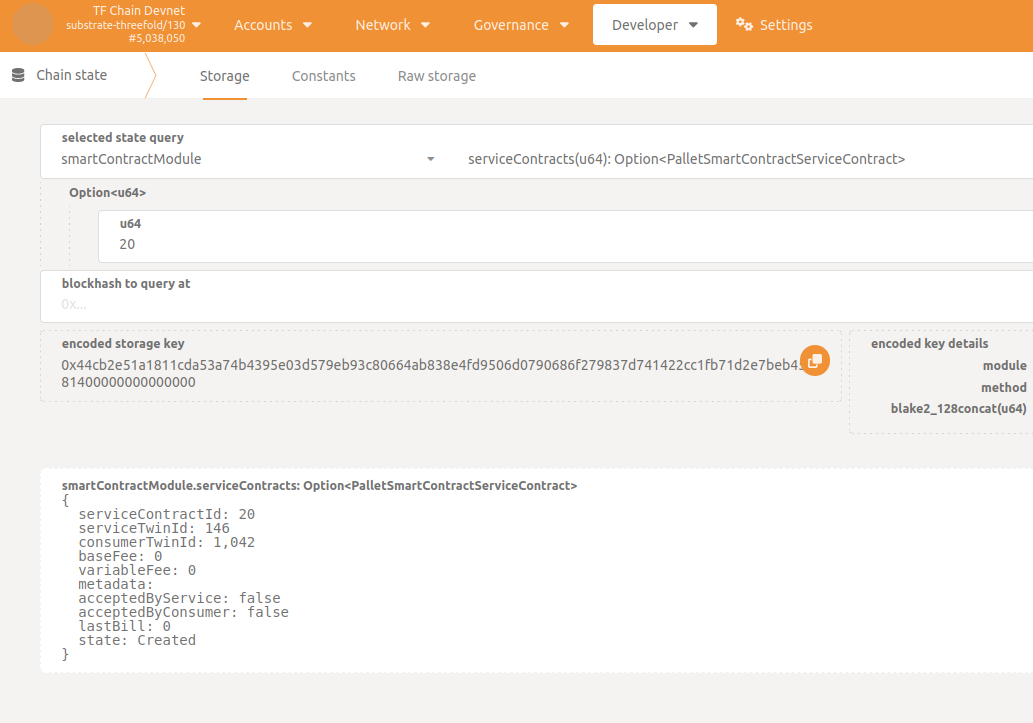
Parse service contract
To get the corresponding contract details, go to Developer -> Chain state -> smartContractModule -> serviceContracts() and provide the contract ID.
You should see the following details:
Check if the contract fields are correct, especially the twin ID of both service and consumer, to be sure you get the right contract ID, referenced as serviceContractId.
Wrong contract ID ?
If twin IDs are wrong (how to get my twin ID?) on service contract fields it means the contract does not correspond to the last created contract.
In this case parse the last contracts on stack by decreasing serviceContractId and try to identify the right one; or the contract was simply not created so you should repeat the creation process and evaluate the error log.
Step 2: Fill contract
Once created, the service contract must be filled with its relative per hour fees:
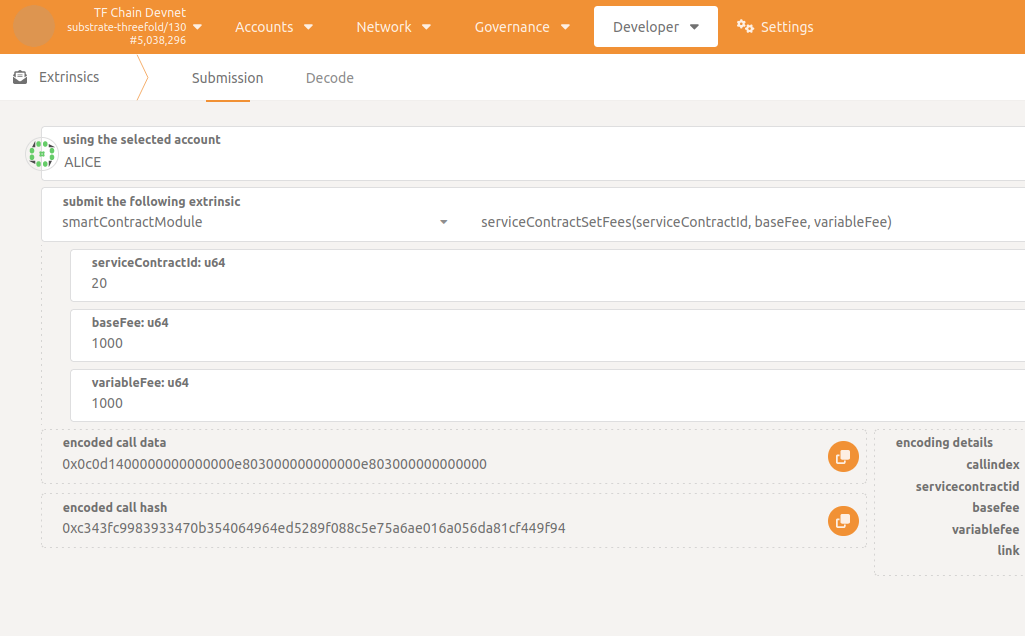
baseFeeis the constant "per hour" price (in TFT) for the service.variableFeeis the maximum "per hour" amount (in TFT) that can be billed extra.
To provide these values (only service can set fees), go to Developer -> Extrinsics -> smartContractModule -> serviceContractSetFees() specifying serviceContractId.
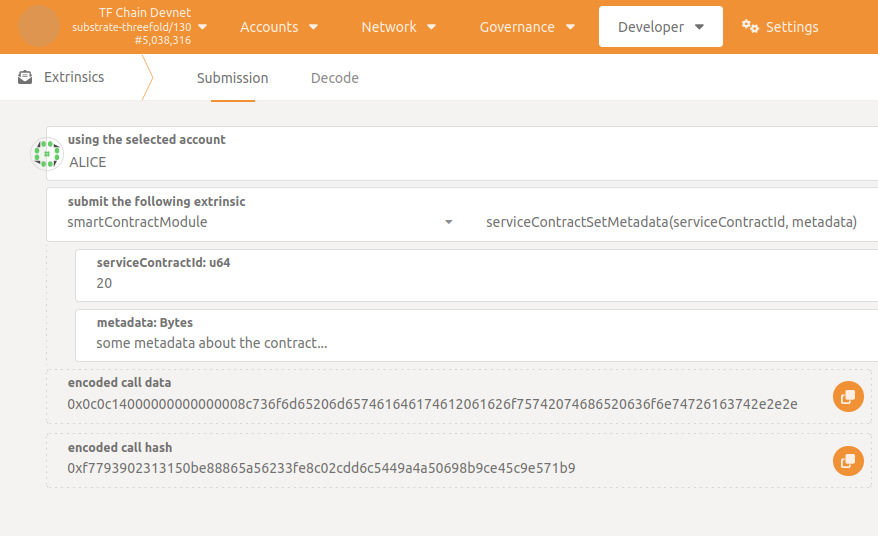
Some metadata (the description of the service for example) must be filled in a similar way (Developer -> Extrinsics -> smartContractModule -> serviceContractSetMetadata()).
In this case service or consumer can set metadata.
The agreement will be automatically considered Ready when both metadata and fees are set (metadata not empty and baseFee greater than zero).
Note that whenever this condition is not reached both extrinsics can still be called to modify agreement.
You can check the contract status at each step of flow by parsing it as shown here.
Step 3: Both parties approve contract
Now having the agreement ready the contract can be submited for approval.
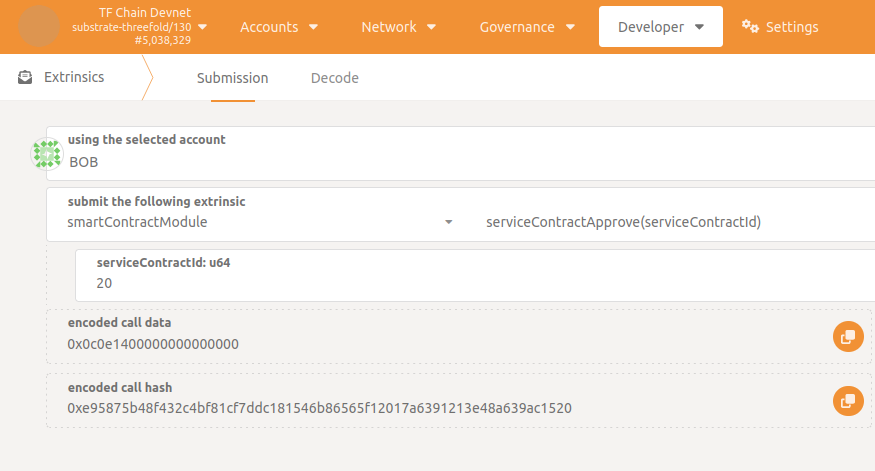
To approve the agreement, go to Developer -> Extrinsics -> smartContractModule -> serviceContractApprove() specifying serviceContractId.
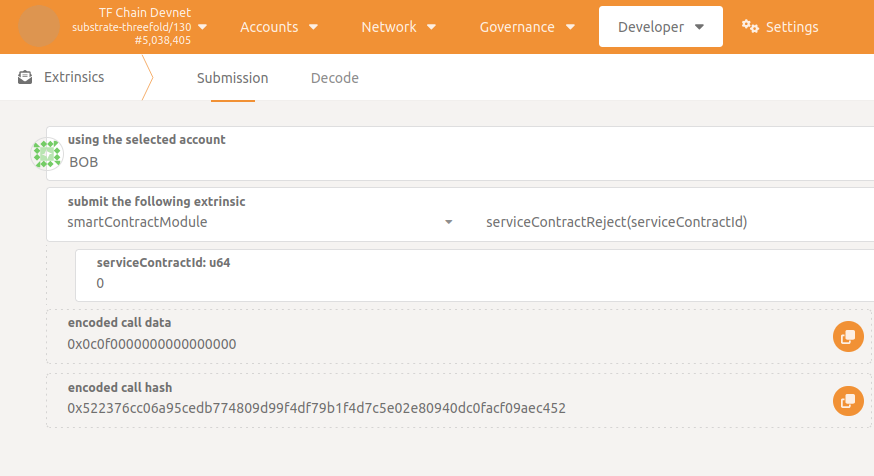
To reject the agreement, go to Developer -> Extrinsics -> smartContractModule -> serviceContractReject() specifying serviceContractId.
The contract needs to be explicitly Approved by both service and consumer to be ready for billing.
Before reaching this state, if one of the parties decides to call the rejection extrinsic, it will instantly lead to the cancelation of the contract (and its permanent removal).
Step 4: Bill for the service
Once the contract is accepted by both it can be billed.
Send bill to consumer
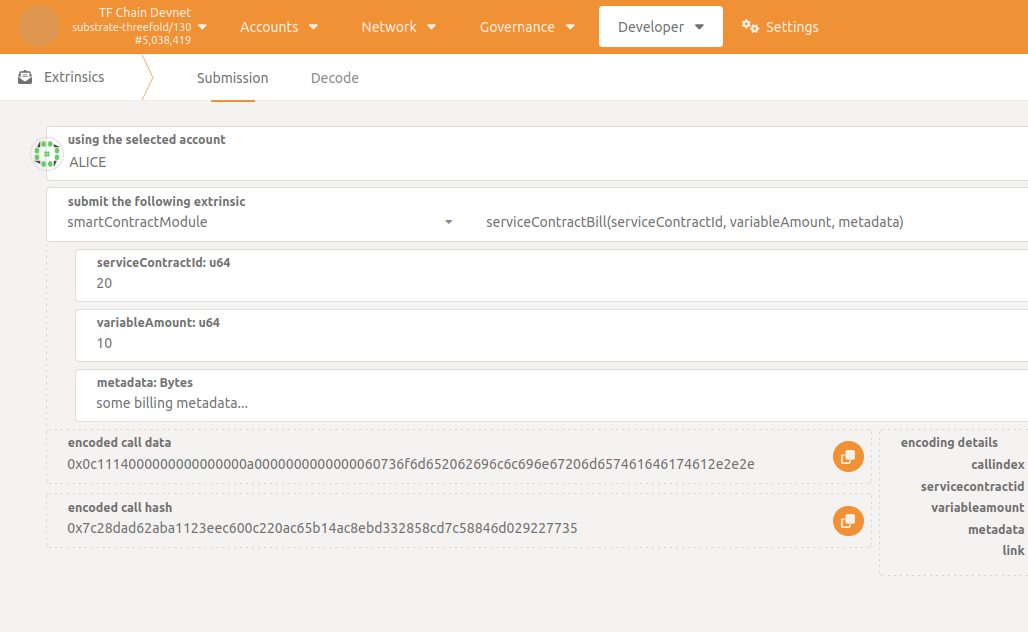
Only the service can bill the consumer going to Developer -> Extrinsics -> smartContractModule -> serviceContractBill() specifying serviceContractId and billing informations such as variableAmount and some metadata.
Billing frequency
⚠️ Important: because a service should not charge the user if it doesn't work, it is required that bills be send in less than 1 hour intervals. Any bigger interval will result in a bounded 1 hour bill (in other words, extra time will not be billed). It is the service responsability to bill on right frequency!
Amount due calculation
When the bill is received, the chain calculates the bill amount based on the agreement values as follows:
amount = baseFee * T / 3600 + variableAmount
where T is the elapsed time, in seconds and bounded by 3600 (see above), since last effective billing operation occured.
Protection against draining
Note that if variableAmount is too high (i.e variableAmount > variableFee * T / 3600) the billing extrinsic will fail.
The variableFee value in the contract is interpreted as being "per hour" and acts as a protection mechanism to avoid consumer draining.
Indeed, as it is technically possible for the service to send a bill every second, there would be no gain for that (unless overloading the chain uselessly).
So it is also the service responsability to set a suitable variableAmount according to the billing frequency!
Billing considerations
Then, if all goes well and no error is dispatched after submitting the transaction, the consumer pays for the due amount calculated from the bill (see calculation detail above). In practice the amount is transferred from the consumer twin account to the service twin account. Be aware that if the consumer is out of funds the billing will fail AND the contract will automatically be canceled.
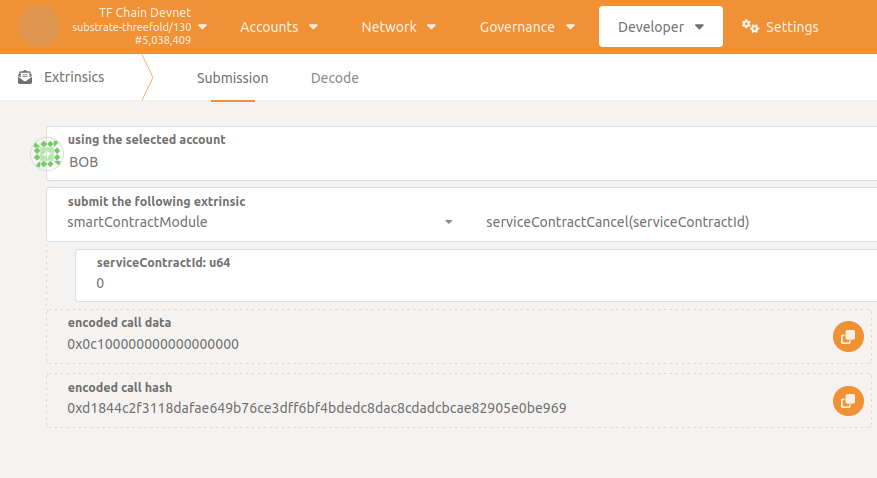
Step 5: Cancel the contract
At every moment of the flow since the contract is created it can be canceled (and definitively removed).
Only the service or the consumer can do it going to Developer -> Extrinsics -> smartContractModule -> serviceContractCancel() specifying serviceContractId.